Gynecomastia Overview
Gynecomastia, often referred to as “man boobs,” or chest fat associated with male breast cancer. It is a common condition that affects a significant number of men worldwide. It is the benign enlargement of male or female breast tissue together, which occurs due to hormonal imbalances or other medical conditions. Gynecomastia can cause physical discomfort, emotional distress, and even impact self-esteem. However, it is treatable and manageable with the right approach.
In this blog post, we will explore the surgical treatment of gynecomastia, its symptoms, causes, and the various treatment options available. We will also dive into statistics, causes, risk factors, and long-term outcomes. Let’s break it down into simpler sections for easy understanding.
What is Gynecomastia and How Do You Get It?
It is the abnormal breast development of breast tissue in men, caused by an imbalance between the estrogen receptors (the female hormone) and androgen receptors and androgen (the male hormone). When estrogen levels increase or androgen levels decrease, men may experience breast tissue growth. This can happen at any age, but it is most common during puberty, middle age, and older adulthood. In some cases, the cause of gynecomastia remains unclear even after thorough evaluations, and these cases are classified as idiopathic gynecomastia.
According to the NIH study, globally, it is estimated that 32-65% of men will experience some degree of gynecomastia during their lifetime. In the United States, gynecomastia affects up to 60% of adolescents during puberty, though many cases resolve naturally without treatment within a few months to two years.
What Happens If a Male Has Gynecomastia?
When a male develops gynecomastia, he may notice gynecomastia symptoms such as swelling in one or both breasts, tenderness in the breast tissue, and increased nipple sensitivity.
While the condition is not life-threatening, it can cause discomfort and self-consciousness, leading to anxiety or even depression in some cases. Many men with gynecomastia report feeling embarrassed, especially in situations where they need to remove their shirts, such as at the beach or pool.
What is Gynecomastia in Bodybuilding?
In the bodybuilding community, gynecomastia often associated with the use of anabolic steroids. Moreover can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance. These steroids increase testosterone levels, which can convert to estrogen in excess, causing breast tissue to develop. This condition referred to as “gyno” by bodybuilders.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, approximately 50% of anabolic steroid users may experience some form of gynecomastia. Many bodybuilders seek treatment to remove the excess tissue, often opting for surgery.
What is Stage 1?
It can progress through different stages, ranging from mild to severe. Stage 1 gynecomastia is the initial phase of breast development, where there is a small enlargement of breast tissue with minimal swelling. It is often reversible with proper treatment and may not require surgical intervention. Early detection and treatment are crucial to preventing further development.
What Percentage of People Have It?
Worldwide, it is estimated that 32-65% of men will develop some form of gynecomastia during their lives. Moreover, 30-40% of men aged 50-70 develop gynecomastia due to hormonal changes that occur with aging.
Is it Normal to Have it at the Age of 21?
Yes, gynecomastia is normal at 21, especially if it started during puberty. Many cases of pubertal gynecomastia resolve naturally, but some may persist into adulthood.
By the age of 21, if the condition hasn’t resolved, medical evaluation is recommended to rule out any underlying issues, such as hormone imbalances or medication side effects.
At What Age Does It Start?
Gynecomastia can occur at any age, but there are three common periods:
Neonatal
Approximately 60-90% of newborn males have transient gynecomastia due to maternal estrogen exposure. This usually resolves within a few weeks of birth.
Puberty
Gynecomastia affects 50-60% of boys during puberty, typically starting between ages 12 and 14. In most cases, it resolves naturally within 6 months to 2 years.
Older Age
Gynecomastia is common in men over 50 due to declining testosterone levels and increased estrogen activity. Studies show that up to 70% of men over the age of 50 experience some form of gynecomastia.
What is the Difference Between Gynecomastia and Chest Fat?
Gynecomastia caused by the growth of glandular breast tissue due to hormonal imbalances, while chest fat, also known as pseudo-gynecomastia, is simply an accumulation of fat in the chest area. The key difference is that gynecomastia involves firm glandular tissue, whereas chest fat is softer and can usually be reduced through exercise and diet.
Is Gynecomastia Common in Teenagers?
Yes, gynecomastia is very common in teenagers. During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can lead to temporary breast enlargement because of breast tissue. Up to 70% of teenage boys experience some degree of gynecomastia. The good news is that most cases resolve naturally as hormone levels stabilize.
How Can It Affect Mental Health?
Gynecomastia can have a profound impact on mental health, especially in adolescents and young adults. Men with gynecomastia often report feelings of embarrassment, social anxiety, and low self-esteem. In severe cases, it can lead to depression or body dysmorphic disorder.
According to a study published in Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, men with gynecomastia are two to three times more likely to experience depression and anxiety compared to men without the condition.
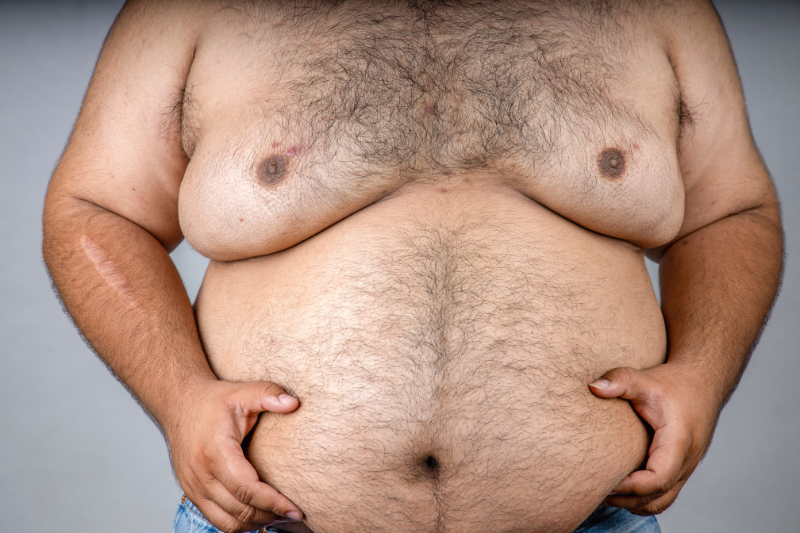
Gynecomastia – Causes and Risk Factors
Who is at High Risk for Gynecomastia?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing it, including:
Age
Men over the age of 50 are at higher risk of male breast and prostate cancer, due to declining testosterone levels.
Obesity
Excess fat can increase estrogen levels, leading to breast tissue growth.
Medications
Certain drugs, including antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and steroids, can cause gynecomastia.
Hormonal Imbalances
Conditions such as hypogonadism or hyperthyroidism can disrupt the balance of testosterone and estrogen.
Substance Abuse
The use of alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroids can increase the risk of developing gynecomastia.
Testicular Tumors
Testicular tumors, such as Leydig cell and Sertoli cell tumors, can lead to increased estrogen production. These tumors influence hormonal levels, resulting in signs like gynecomastia.</p>
Will Increasing Testosterones Reduce Gynecomastia?
In some cases, more testosterone can help with gynecomastia if it’s caused by low testosterone. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can help balance the hormones and shrink the breast tissue. But TRT isn’t always the solution and in some cases can make gynecomastia worse if too much testosterone is converted to estrogen.
Can You Fix Gynecomastia Naturally?
In mild cases of androgen deficiency, gynecomastia can be improved through natural methods such as:
Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy weight and reducing body fat can help balance hormone levels and reduce breast tissue.
Avoiding Alcohol and Drugs
Limiting the use of alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroids can help prevent and reduce gynecomastia.
Herbal Supplements
Some studies suggest that natural supplements like zinc and vitamin D may help support testosterone production, though more research is needed.

Can Medications Cause Gynecomastia?
Yes, several medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect. These include:
Antidepressants
Certain SSRI medications have been linked to gynecomastia.
Anti-anxiety Medications
Drugs like diazepam can cause hormonal imbalances.
Steroids
Anabolic steroids used for bodybuilding can lead to gynecomastia due to the conversion of excess testosterone into estrogen.
Anti-androgens
Drugs used to treat prostate cancer and breast cancer can reduce testosterone levels, leading to gynecomastia and breast pain.
How Does Hormone Imbalance Lead to Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia occurs when there is an imbalance between estrogen and androgen levels. Estrogen promotes the growth of breast tissue, while androgen inhibits it. If estrogen levels are too high or androgen levels are too low, breast tissue may enlarge.
This hormonal imbalance can result from various factors, including puberty, aging, medication use, and certain medical conditions. The pituitary gland regulates hormone levels, and tumors of the pituitary gland can influence these levels, potentially leading to conditions like gynecomastia.
Can Anabolic Steroids Cause Gynecomastia?
Yes, anabolic steroids are a common cause of gynecomastia, particularly in bodybuilders. Steroids increase testosterone levels, which can be converted into estrogen through a process called aromatization. The excess estrogen then stimulates the growth of breast tissue, leading to gynecomastia.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, up to 50% of anabolic steroid users experience gynecomastia.
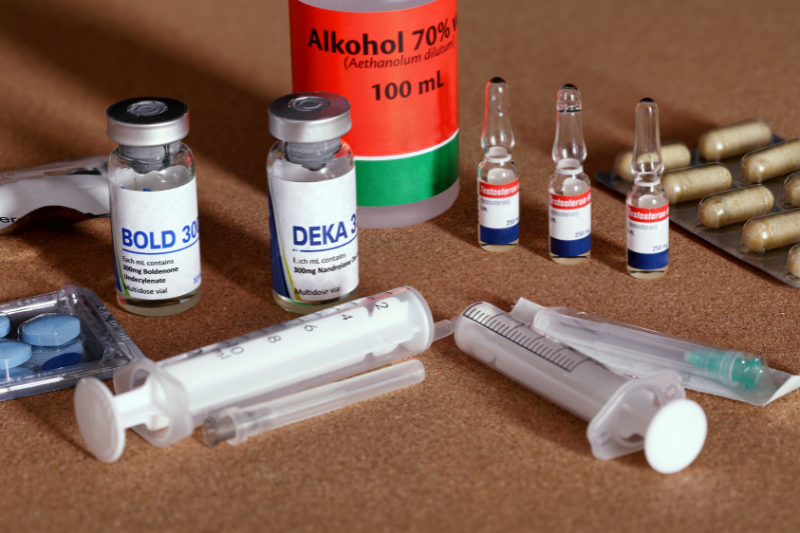
Gynecomastia – Diagnosis and Symptoms
How Do You Know If You Have Gynecomastia?
The main symptom is the enlargement of breast tissue in one or both breasts. Common gynecomastia symptoms include breast enlargement, tenderness, and nipple sensitivity. The breast may feel firm or rubbery, and there may be tenderness or sensitivity around the nipple.
In some cases, a small, disc-shaped lump can be felt under the nipple. If you suspect you have gynecomastia, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
How to Deal with Gynecomastia?
Dealing with gynecomastia starts with addressing the underlying cause. For mild cases, lifestyle changes such as losing weight, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol and drugs can help.
For more severe cases, medical treatment or surgery may be necessary. It’s also important to seek emotional support, as chronic gynecomastia also can impact mental health.
What Are the Symptoms of Gynecomastia vs. Pseudogynecomastia?
While both involve breast enlargement because of the chest area, the key difference is the type of breast enlargement and breast tissue proliferation involved. Gynecomastia involves the growth of glandular breast tissue, which feels firm and rubbery, whereas pseudo gynecomastia is caused by excess fat, which feels soft and can be reduced through diet and exercise.
How Can You Tell the Difference Between Gynecomastia and Muscle Growth?
Muscle growth in the chest area typically occurs as a result of strength training and exercise, whereas that associated with gynecomastia often involves the growth of breast tissue. Men with gynecomastia may notice a rounded or swollen appearance of the chest, along with tenderness around the nipple. In contrast, muscle growth will result in a more defined, firm chest without tenderness.

Gynecomastia – Treatment Options
Can Gynecomastia Be Treated?
Yes, surgeons can treat it. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. For mild cases, lifestyle changes and hormone therapy may be effective. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the excess breast tissue.
How Do Men Fix Gynecomastia?
There are several treatment options, including:
Medications
Hormone therapy or medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) may be used to reduce breast tissue growth.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery, such as liposuction or mastectomy, may be required to remove the excess tissue.
Lifestyle Changes
Losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding substances that contribute to hormonal imbalances can help reduce or prevent gynecomastia.
Can It Be Reversed?
In many cases yes, gynecomastia can be reversed especially if it’s caused by temporary factors like puberty or medication use. But if it’s caused by long-term hormonal imbalances or other medical conditions then treatment is needed to reduce or get rid of the breast tissue.
Can You Self-Treat It?
Mild gynecomastia can be managed with lifestyle changes like losing weight, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol and drugs. However, you should consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause of the condition and get proper guidance on treatment options.
Gynecomastia – Long-Term Outcomes and Severity
Does Gynecomastia Go Away?
In many cases, it goes away on its own especially caused by hormonal changes during puberty. But if it persists into adulthood then surgeons recommend a treatment to reduce the risk of breast cancer in tissue.
Does Gyno Go Away?
Yes, gyno (gynecomastia) often goes away on its own, especially in adolescent boys. If it doesn’t resolve naturally then treatment options like medication or surgery may needed.
Is Gynecomastia a Serious Condition?
It is not life-threatening but can be life-altering. Men can experience physical and emotional pain and the condition can affect self-esteem and body image.
Is Gynecomastia in Men Reversible?
In many cases, gynecomastia in men is reversible, especially if it is caused by temporary factors like medication use or hormonal changes during puberty. However, long-standing cases may require medical treatment or surgery.
Does It Come Back After Treatment?
It can come back after treatment if the underlying cause of chronic kidney disease is not addressed. For example, if the condition is caused by medication or substance use, it may return if the individual continues using those substances. In cases where surgery is performed, recurrence is rare, but it is possible if the hormonal imbalance persists.
How Long Does It Take to Recover from the Surgery?
Recovery from gynecomastia surgery typically takes 4 to 6 weeks. Most men can return to work within a few days. Nonetheless, avoiding strenuous activities for several weeks allows proper healing.
Can Untreated Gynecomastia Cause Other Problems?
While it is not dangerous, leaving it untreated can have physical and emotional consequences. Furthermore. it can cause chronic tenderness or pain in the breast tissue. Emotional, men can struggle with low self-esteem, social anxiety, and body image issues because of their chest. In severe cases, these can lead to depression or body dysmorphic disorder.
Also in some cases, it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. For example, hormone-producing tumors, liver disease, or thyroid disorders can also cause gynecomastia through hormonal imbalances that lead to breast tissue growth. So if it appears suddenly or persists, seek medical attention as a doctor can rule out any serious condition.
What Are the Surgical Options?
For men with severe or long-lasting gynecomastia breast or prostate cancer, that doesn’t respond to non-surgical treatments, surgery may be the best option. The two most common types of surgical procedures are:
Liposuction
Surgeons recommend this procedure to remove excess fat in the chest area. Typically suitable for men who have pseudo-gynecomastia. A male breast cancer that involves chest fat rather than glandular tissue.
Mastectomy
This procedure involves the surgical removal of the glandular breast tissue that causes gynecomastia. The surgeon usually performs surgery through small incisions around the nipple, which minimizes scarring. Mastectomy is a more invasive procedure but offers a permanent solution.
Daddy-Do-Over
A “daddy-do-over” is a collection of cosmetic procedures aimed at helping men restore a youthful appearance and achieve various aesthetic goals. This approach often addresses the physical changes that can come with aging, weight fluctuations, or parenthood. Commonly recommended procedures in a daddy-do-over may include:
Tummy Tuck
The tummy tuck procedure tightens the abdominal muscles and removes excess skin for a firmer midsection.
Liposuction
The liposuction procedure targets areas like the abdomen, flanks (love handles), and inner thighs to remove stubborn fat and enhance body contours.
Gynecomastia Surgery
Male breast reduction procedure reduces excess breast tissue in men, providing a more sculpted chest.
All these procedures standalone or combined have high success rates, and most men report significant improvements in their physical appearance and self-confidence after surgery. For a single procedure, the recovery period is typically 4-6 weeks. And most men can return to their normal activities within a week. Although combined procedures require longer recovery time. Regardless, surgeons recommend avoiding strenuous exercise during the recovery phase.
Can Weight Loss Get Rid of Gynecomastia?
Weight loss can get rid of pseudogynecomastia. Particularly caused by fat accumulation in the chest area. But if caused by glandular tissue growth (true gynecomastia) then weight loss won’t get rid of the problem.
Exercise and weight management are important for overall health but in the case of true gynecomastia the breast tissue won’t decrease much with weight loss alone.
What Medications Are Used to Treat It?
Medications can be an option, especially in the early stages. Common medications treatment for are:
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
Drugs like tamoxifen shrink breast tissue in men with gynecomastia. They block the effects of estrogen on breast tissue which can reverse the growth.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Medications like anastrozole reduce estrogen production in the body. Eventually helpful in cases where gynecomastia caused by high estrogen levels.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
For men having low testosterone levels, TRT can help balance hormone levels and reduce breast tissue growth. However, TRT not always effective and can sometimes worsen gynecomastia if the excess testosterone converted into estrogen.
Are There Non-Surgical Treatments?
Yes, there are several non-surgical treatments, especially in its early stages. These include:
Hormone Therapy
Balancing hormone levels through medications like SERMs or aromatase inhibitors can help reduce breast tissue growth.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol, marijuana, and anabolic steroids, and adopting a balanced diet can help prevent and reduce gynecomastia.
Cold Compresses and Pain Management
For men who experience tenderness or discomfort in the chest area, cold compresses, and over-the-counter pain relievers can provide relief.
In mild cases, non-surgical treatments may be enough to manage the condition. However, for men with more severe conditions, surgery may be the only permanent solution.
Gynecomastia and Male Breast Cancer FAQs
Can Gynecomastia Lead to Male Breast Cancer?
It is not a direct cause of male breast cancer. However, both conditions involve changes in breast tissue, and having gynecomastia does not increase a man’s risk of developing breast cancer. It’s important to distinguish between gynecomastia, in which the breast gland tissue is benign (non-cancerous), and breast cancer, which requires medical intervention.
How Can You Tell the Difference Between Gynecomastia and Male Breast Cancer?
It usually presents as a soft, symmetrical swelling of the breast tissue, which can sometimes be tender or painful. In contrast, male breast cancer often feels like a hard or firm lump that may be painless.
Breast cancer can also cause changes in the skin around the nipple, such as dimpling, retraction, or discharge. If you notice any unusual lumps or skin changes, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
How Can You Tell the Difference Between Gynecomastia and Male Breast Cancer?
It usually presents as a soft, symmetrical swelling of the breast tissue, which can sometimes be tender or painful. In contrast, male breast cancer often feels like a hard or firm lump that may be painless. Breast cancer can also cause changes in the skin around the nipple, such as dimpling, retraction, or discharge. If you notice any unusual lumps or skin changes, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Should Men with Gynecomastia Be Screened for Breast Cancer?
Routine breast cancer screening typically not recommended for men with gynecomastia. Unless they have additional risk factors, such as a family history of breast or prostate cancer patients or genetic predispositions like BRCA mutations. If you fall into a higher-risk category, talk to your doctor about potential screening options.
What Are the Signs of Male Breast Cancer I Should Watch For?
Key signs of male breast cancer include a firm lump in the breast, changes in the appearance of the breast or nipple, nipple discharge (especially if bloody), or skin changes like dimpling or redness. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider right away.
Gynecomastia is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. While it is not life-threatening, it can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress. The good news is that it is treatable, and there are several options available depending on the severity of the condition. From lifestyle changes, and medication to surgery, men can take control of their condition and improve their quality of life.
Individuals suspecting having gynecomastia, consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options. Addressing the issue early can help prevent further development and alleviate any mental health challenges associated with the condition.